Build a GSM Network with OpenBSC OsmoBTS OsmoTRX and USRP B210 on a Single PC
Build a GSM Network with OpenBSC OsmoBTS OsmoTRX and USRP B210 on a Single PC
This document assumes that you have basic knowledge of the GSM network architecture(MSC, BTS, Abis, Um, etc.), Linux terminal and USRP UHD driver.
Environment
- Intel Core i5-6500 CPU, 8 GB RAM, 64 GB HDD, Ethernet Connection, USB 3.0 Port
- Ubuntu 16.04.4 Desktop 64-bit
- USRP B210, Two GSM Antennas
Structure
GSM Network
As for our GSM network, USRP B210, OsmoTRX and OsmoBTS consist the BTS(Base Transceiver Station),
OpenBSC running as OsmoNITB (Network In The Box) implements a minimal subset of the BSC, MSC, SMSC and HLR.
OsmoTRX
OsmoTRX is a software-defined radio transceiver that implements the Layer 1 physical layer of a BTS.

It is the bridge between the RF hardware(USRP B210 in our case) and the OsmoBTS.
OsmoBTS
OsmoBTS is a software implementation of a GSM BTS.
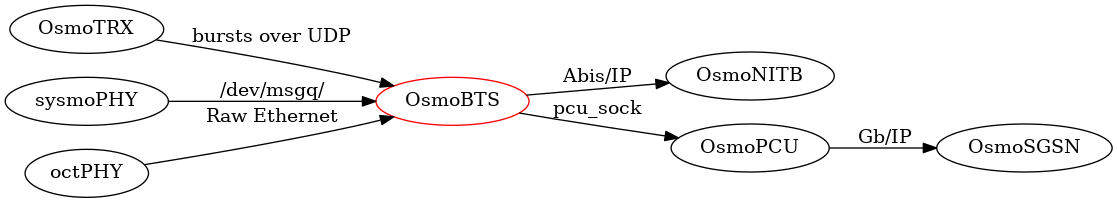
OsmoBTS is modular and has support for multiple back-ends.
A back-end talks to a specific L1/PHY implementation of the respective BTS hardware.
In our case, OsmoBTS(osmo-bts-trx) talks to the OsmoTRX radio transceiver running on USRP B210.
OpenBSC
OpenBSC started as a BSC (Base Station Controller) side implementation of the A-bis protocol,
It can run either as OsmoBSC, exposing an A interface towards an external MSC,
or as OsmoNITB (Network In The Box), whert implements a minimal subset of the BSC, MSC, SMSC and HLR.
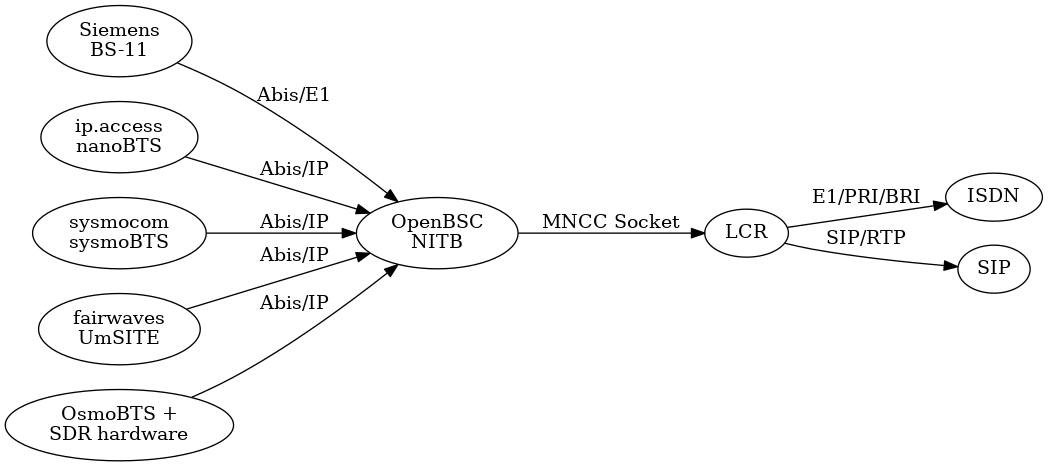
As our GSM network runs on a single PC, OpenBSC runs here as OsmoNITB.
It talks to OsmoBTS through Abis/IP.
USRP B210
USRP B210 is a SDR(Software Define Radio) kit from Ettus.
It transforms the digital signal on our computer into real world radio signal.
Installation
Osmocom recommands that you should use your distribution’s package management system for installing stuff.
As we will tinker with the source code later, so OpenBSC is built with make.
As for OsmoBTS and OsmoTRX, you should install them from the Osmocom repository.
Will come to that later.
Set up our working directory as non-root user
mkdir ~/Projects
cd ~/Projects
OpenBSC
First install these dependencies:
sudo apt install libdbi-dev libdbd-sqlite3 libortp-dev build-essential libtool autoconf autoconf-archive automake git-core pkg-config libtalloc-dev libpcsclite-dev libpcap-dev
Then, build these projects bellow from source, following the Build from Source guide.
- libosmocore
- libosmo-abis
- libosmo-netif
- openbsc
For each project
git clone git://git.osmocom.org/[project name]
cd [project name]
autoreconf -fi
./configure
make
make check
sudo make install
sudo ldconfig -i
In case of any missing dependency, ./configure will tell you.
Note: For openbsc, you have to run cd openbsc/openbsc instead of cd openbsc.
OsmoBTS
As I have said earlier, installing from the Osmocom repository is preferred if you have no special excuse.
sudo su
wget http://download.opensuse.org/repositories/network:/osmocom:/latest/xUbuntu_16.04/Release.key
apt-key add Release.key
rm Release.key
echo "deb http://download.opensuse.org/repositories/network:/osmocom:/latest/xUbuntu_16.04/ ./" > /etc/apt/sources.list.d/osmocom-latest.list
exit
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install osmo-bts-trx
If you should build it from source, make sure adding --enable-trx for ./configure.
The other building process are the same with the above.
OsmoTRX & UHD
I had no luck building OsmoTRX from source, neither with UHD from Ettus PPA, nor UHD built from source.
Past experiences tell me that the installation of UHD is very tricky.
At last, I just install UHD and OsmoTRX from the Ubuntu repository.
sudo apt-get install osmo-trx libuhd-dev uhd-host
Configuration
OpenBSC
Almost each Osmocom program has the configuration examples. Just look for ‘doc/examples/’.
If you have built OpenBSC from source
mkdir ~/.osmocom/
cp ~/Projects/openbsc/openbsc/doc/examples/osmo-nitb/sysmobts/openbsc.cfg ~/.osmocom/
No need to change the openbsc.cfg file here.
OsmoBTS
If you have built OsmoBTS from source
cp ~/Projects/osmo-bts/doc/examples/calypso/osmo-bts.cfg ~/.osmocom/
Delete osmotrx legacy-setbsic from phy 0.
OsmoTRX
OsmoTRX can be configured with a variety of options on the command line. In most cases, the default settings will suffice.
Running
Open a shell and start OpenBSC
sudo osmo-nitb -c ~/.osmocom/openbsc.cfg
Open a shell and start OsmoBTS
sudo osmo-bts-trx -c ~/.osmocom/osmo-bts.cfg
Open a shell and start OsmoTRX
sudo osmo-trx
Search ‘Available networks’ from your phone, and you should seen Test PLMN 1-1 2G among local networks.
Reference
- https://github.com/samatt/SDR-101/blob/master/running_osmobts_with_usrp1_ubuntu_12.04.md
- https://osmocom.org/projects/openbsc/wiki/OpenBSC
- https://osmocom.org/projects/openbsc/wiki/Building_OpenBSC
- https://osmocom.org/projects/cellular-infrastructure/wiki/Build_from_Source
- https://osmocom.org/projects/osmobts/wiki/Wiki
- https://cn0xroot.com/2017/04/11/getting-started-with-3g-ip-access-nano3gopenbscosmocom-bb-part-1/
- https://osmocom.org/projects/osmotrx/wiki/OsmoTRX
- https://osmocom.org/projects/baseband/wiki/CalypsoBTS